Annuity Basics
- What are annuities?
- How do annuities work?
- Which type of annuity is right for you?
With 60% of people concerned they might outlive their retirement resources, annuities can provide the guaranteed1 income that 99% of savers say would help them feel secure2.
Let’s break down a few annuity essentials: what are they, how do they work, and which one is right for you?
Types of Annuities
VA
Variable Annuities3
allow investment in various funds for potential growth
FIA
Fixed Indexed Annuities
combine the safety of fixed returns with the potential for higher gains linked to a market index — without investing in the market or an index
RILA
Registered Index
Linked Annuities4
(RILAs) offer the potential for higher growth linked to market performance with partial downside protection
How do annuities compare to other financial products?
| Features | Annuities | IRAs | CDs | Muni Bonds | Govt. Bonds | EE Bonds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Deferral | Yes | Yes | No | N/A | No | Yes |
| Tax-Free | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Tax-Deductible | No | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Market Risk | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Safety of Principal | Safe | Varies | Safe | Varies | Safe | Safe |
| Surrender Charge(s) on Early Withdrawal | Based on Contract | Possible back-end sales charge | Penalties | None | None | Moderate |
| Tax Penalties on Early Withdrawal | Possibly Harsh | Possibly Harsh | None | None | None | None |
Are annuities risky?
There are several options to consider when looking for growth opportunities—
all of which come with varied return potential and risk.
Here are where several types of annuities fit on the risk-return spectrum.
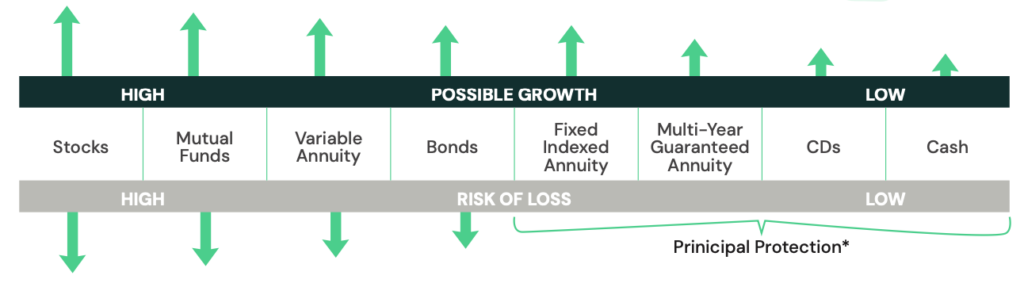
Regardless of economic conditions, your money grows based on the terms of your contract. Additionally, it’s important to know that a contract with Guaranty Income Life won’t lose value because of market downturns.
Before Purchasing an Annuity
Assess
Assess Your Financial Goals with Your Financial Professional: Consider your income needs and retirement plans.
Choose
Choose the Right Type of Annuity: Decide which type of annuity suits your financial situation and goals.
Select
Select a Provider: Look for a reputable insurance company with strong financial ratings, like Guaranty Income Life.
Purchase
Purchase Your Annuity: Work with a financial professional to purchase an annuity from Guaranty Income Life.
FAQs
What is a tax-deferred annuity?
A tax-deferred annuity allows your savings to grow tax-free until withdrawal, helping you save more for retirement. This means you only pay taxes when you take money out, typically during retirement.
Is a tax-deferred annuity a good idea?
A tax-deferred annuity may be a good idea if you want to grow your retirement savings without paying taxes on the earnings until you withdraw them. It offers potential for tax-efficient growth and a steady income stream in retirement.
Is a tax-deferred annuity the same as a 401(k)?
No, a tax-deferred annuity is not the same as a 401(k). A 401(k) is an employer-sponsored retirement plan for pre-tax dollars, while a tax-deferred annuity is a contract with an insurance company to provide future income and is often purchased with after-tax dollars.
How does a deferred annuity work?
A deferred annuity allows you to pay money into the contract that grows tax-free until you withdraw it. During the accumulation phase, your contributions grow, and in the payout phase, you can receive regular income, typically during retirement.
What is the disadvantage of tax-deferred?
One disadvantage of tax-deferred annuities is that while you defer taxes on earnings until withdrawal, you may end up paying higher taxes later if your tax rate increases in retirement. Additionally, early withdrawals before age 59½ may incur a 10% IRS penalty.
Is an annuity a good product?
An annuity may be a good choice for those seeking a reliable, steady income stream in retirement, but it may not be suitable for everyone. It’s important to consider factors like fees, surrender charges, and your individual financial goals before deciding.
What are the disadvantages of an annuity?
Disadvantages of annuities can include fees, surrender charges for early withdrawals, and limited liquidity. Additionally, the returns may be lower compared to actual investments, and some annuities can be complex and difficult to understand.
Who should buy an annuity?
Annuities are best suited for individuals looking for a guaranteed* income stream in retirement, those who want to manage longevity risk, and those seeking tax-deferred growth. They can be particularly beneficial for conservative savers who prioritize financial security over higher returns.
*Annuity Guarantees rely on the financial strength and claims-paying ability of the issuing insurer.
Who should not buy an annuity?
Individuals who need immediate liquidity, prefer high-growth investments, or have a short investment horizon should not buy an annuity. Additionally, those uncomfortable with the fees and complexities associated with annuities may want to explore other financial options.
At what age should I buy an annuity?
The ideal age to buy an annuity varies, but many people consider purchasing one in their 50s or 60s when they are approaching retirement and looking to secure a guaranteed* income stream.
*Annuity Guarantees rely on the financial strength and claims-paying ability of the issuing insurer.
How much does an annuity pay per month?
The monthly payment from an annuity depends on factors such as the amount contributed, the type of annuity, the payout option chosen, and the age and gender of the annuitant.
Where can I buy an annuity?
You can buy an annuity through insurance companies, financial advisors, banks, and online financial platforms. It’s important to compare options and seek advice from a trusted financial professional to find the best annuity for your needs. All annuities are issued by insurance companies.
Is an annuity the same as an IRA (Individual Retirement Account)?
No, an annuity is not the same as an IRA. An annuity is an insurance product that provides a guaranteed* income stream, while an IRA is a retirement savings account offering tax advantages. However, you can fund an annuity within an IRA.
*Annuity Guarantees rely on the financial strength and claims-paying ability of the issuing insurer.
How do I make money in an annuity?
You make money in an annuity through interest or investment gains on the principal amount, depending on the type of annuity. Fixed annuities offer guaranteed* interest rates, while variable and indexed annuities provide returns partially or fully based on market performance or a specific index. Over time, these earnings compound tax-deferred until withdrawal.
*Annuity Guarantees rely on the financial strength and claims-paying ability of the issuing insurer.
How much does an annuity cost?
The cost of an annuity varies based on factors like the type of annuity, the amount of the initial purchase, and the cost of any additional features or riders. Typically, you can purchase an annuity with a lump sum ranging from $10,000 to over $1 million, and there may be ongoing fees.
Note that while most fixed rate annuities do not charge a fee, some annuities may include a fee, which could vary depending on optional features.
Glossary of Terms

Accumulation Period
The time prior to an annuity’s payout period when money builds up in the annuity contract.
Annuitant
The person whose life expectancy is used to determine the payout of an annuity.
Annuitization
Converting the value of an annuity contract into a stream of income payouts.
Annuity
A retirement product that allows you to save for your future on an income-tax-deferred basis and then allows you to choose a payout option that best meets your need for income when you retire – lump sum, income for life, or income for a certain period of time.
Deferred Annuity
A contract in which annuity payouts begin at a future date.
Effective Annual Yield
Most companies compound and credit interest daily. The rate shown is the effective annual yield after compounding the daily nominal rate. Some companies pay a first-year bonus on their interest to encourage new business. The Effective Annual Yield (EAY) includes the bonus.
- Rate Bonus – Some annuities pay a bonus on the base rate. For example, if the base rate is 3.00% and there is a 1.00% first-year bonus, the EAY for year one will be 4.00%.
- Premium Bonus – Some annuities pay an upfront premium bonus. For example, if the base rate is 3.00% with a 1.00% premium bonus, due to compounding interest, 4.03% will be shown as the Effective Annual Yield.
Equity-Indexed Annuity
An equity-indexed annuity, now more commonly referred to as a fixed indexed annuity, is a type of annuity that credits interest based on the performance of a specified market index, such as the S&P 500®, while providing a guaranteed* minimum interest rate. This allows for potential market-linked growth without the risk of loss of principal.
*Annuity Guarantees rely on the financial strength and claims-paying ability of the issuing insurer.
Fixed Annuity
An annuity contract in which the premiums you pay are credited with a fixed rate of return by the life insurance company, and the company guarantees* a fixed payout every month.
*Annuity Guarantees rely on the financial strength and claims-paying ability of the issuing insurer.
Flexible-Premium Deferred Annuity
A type of annuity that allows you to make multiple contributions over time, rather than a lump-sum payment. The earnings grow tax-deferred until you begin withdrawals, typically in retirement, providing a future income stream.
Illustration
An illustration provides detailed information about how a financial product may perform over time, including how it performed in the past. However, past performance is not an indicator of how it will perform in the future.
Immediate Annuity
A contract in which annuity payments are made at the end of each payment period. Payment periods may be monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually.
Initial Interest Rate
The initial interest rate is determined by prevailing fixed rates. After the specified period, the insurance company may change the interest rate to match current rates, but it would never be below a minimum rate specified in the contract.
Loads, Sales & Maintenance Fees
There are no front-end sales charges with most annuities. If $10,000 is contributed to an annuity, the full $10,000 will be earning interest.
Market Value Adjustment
Some annuities include a Market Value Adjustment (MVA) if surrendered.
- If the contract rate is higher than current rates on new money, a positive MVA adjustment may be made in the cash value. Therefore, if rates go down after the purchase date, the penalty will be less than shown.
- If the contract rate is lower than current rates on new money, a negative adjustment is made in the cash value. Therefore, if rates go up after the purchase date, the surrender penalty will be higher than shown.
Minimum Guaranteed Interest Rate
This minimum rate guarantee* serves two purposes:
- It provides a minimum interest rate an insurance company may credit to an annuity after the initial rate period.
- It is also the rate that insurance company actuaries use to calculate reserve obligations in order to meet state insurance law requirements.
*Annuity Guarantees rely on the financial strength and claims-paying ability of the issuing insurer.
Payout Period
The period during which you receive the income from your annuity contract.
Principal
The amount you pay into your annuity contract as distinguished from the earnings that are credited to it. This may also be referred to as purchase payments, premiums, or contributions.
Rate Hold (on Rollovers)
If you rollover an existing annuity to a new annuity with a different insurance company, the new company will normally hold the beginning rate for a period of time. If the money is not received from the old company within that period, the new annuity will receive the rate in effect on the date the money is received.
Surrender Penalty
Penalty applied to any amount exceeding the Free Annual Withdrawal Amount or to multiple withdrawals within the same contract year if they are not allowed by the terms specified in the contract. In some cases, if the entire annuity is surrendered, the penalty will be applied to the full value of the annuity.
Some annuities include a Market Value Adjustment (MVA) if surrendered.
- If the contract rate is higher than current rates on new money, a positive MVA adjustment may be made in the cash value. Therefore, if rates go down after the purchase date, the penalty will be less than shown.
- If the contract rate is lower than current rates on new money, a negative adjustment is made in the cash value. Therefore, if rates go up after the purchase date, the surrender penalty will be higher than shown.
Penalty Waived at Death
Some annuities waive all surrender penalties in the event of death of the annuitant or some waive penalties at death of the owner. Some waive penalties at the death of owner or annuitant. Some annuities do not waive penalties at death of the owner or annuitant, unless a payout of five years or longer is elected.
Waiver of Surrender Charges
Most companies waive the surrender penalty if the cash value is paid out over a period of time or annuitized, usually five years or longer.
Variable Annuity
A variable annuity3 is a type of annuity contract where the returns are based on the performance of investment options. The value of the annuity can fluctuate, offering the potential for higher returns but also carrying investment risk.
Annuity Calculators

See how annuities can enhance your retirement planning with our interactive calculators. Compare the benefits of tax-deferred annuities versus taxable accounts, explore how tax advantages can boost your savings, and estimate how long your retirement income will last.
While these tools provide valuable insights, partnering with a financial professional will help you tailor these results to your unique needs and build a strategy that ensures your savings last. Use our calculators as a starting point—and get expert guidance to secure your financial future.
FOOTNOTES
1 Annuity Guarantees rely on the financial strength and claims-paying ability of the issuing insurer.
2 2024 Read on Retirement survey | BlackRock
3 Guaranty Income Life does not offer variable annuities.
4 Guaranty Income Life does not offer registered index linked annuities.

